Development - Advanced, exercise 4
Text
The Sørensen–Dice coefficient is a statistic that can be used for comparing the similarity of two strings. Sørensen–Dice’s formula for comparing two input strings x and y is defined as follows:
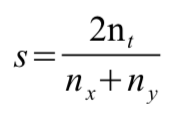
where nt is the number of bigrams found in both strings, nx is the number of bigrams in string x, and ny is the number of bigrams in string y. The bigrams of a string is a list of all the pairs of two consecutive characters that the string contains. For instance, the bigrams of the string "mickey" is the list ["mi", "ic", "ck", "ke", "ey"]. Provided this definition, the Sørensen–Dice coefficient of the strings "mine" and "finest" is 0.5.
Write the Python function def sd(x, y) which takes two strings x and y as input and returns their Sørensen–Dice coefficient.
Solution
# Test case for the function
def test_sd(x, y, expected):
result = sd(x, y)
if expected == result:
return True
else:
return False
# Code of the function
def bigrams(s):
bigram_list = list()
bigram = ""
for c in s:
bigram += c
if len(bigram) == 2:
bigram_list.append(bigram)
bigram = bigram[1:]
return bigram_list
def sd(x, y):
b1 = bigrams(x)
b2 = bigrams(y)
nt = 0
for cur_b in b1:
if cur_b in b2:
nt += 1
return (2 * nt) / (len(b1) + len(b2))
# Tests
print(test_sd("Finest", "Mine", 0.5))
print(test_sd("Finest", "Finest", 1.0))
Additional material
The runnable Python file is available online.