Development - Intermediate, exercise 3
Text
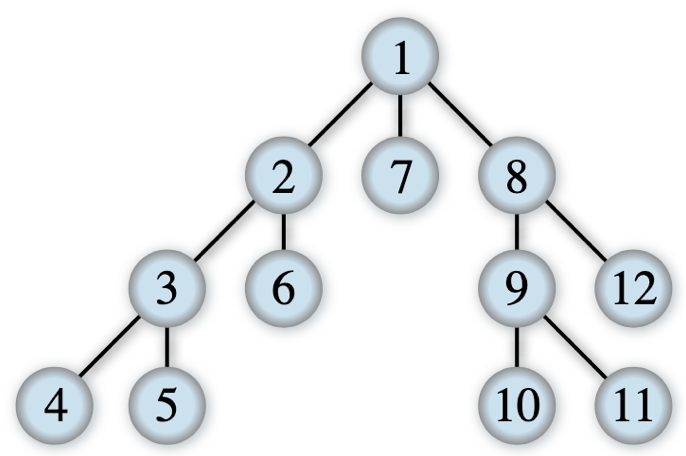
Write the body of the Python function def depth_first_visit(node) that takes the root node of a tree as input and returns the list of all its nodes ordered according to a depth-first visit. The depth-first visit proceeds as indicated in the image below, created by Alexander Drichel, where the numbers indicate the order in which the nodes should be visited.
Solution
from anytree import Node
# Test case for the function
def test_depth_first_visit(node, expected):
result = depth_first_visit(node)
if expected == result:
return True
else:
return False
# Code of the function
def depth_first_visit(node):
result = list()
depth_first_visit_recursive(node, result)
return result
def depth_first_visit_recursive(node, list):
list.append(node)
for child in node.children:
depth_first_visit_recursive(child, list)
# Tests
n1 = Node(1)
n2 = Node(2, n1)
n3 = Node(3, n2)
n4 = Node(4, n3)
n5 = Node(5, n3)
n6 = Node(6, n2)
n7 = Node(7, n1)
n8 = Node(8, n1)
n9 = Node(9, n8)
n10 = Node(10, n9)
n11 = Node(11, n9)
n12 = Node(12, n8)
print(test_depth_first_visit(n1, [n1, n2, n3, n4, n5, n6, n7, n8, n9, n10, n11, n12]))
Additional material
The runnable Python file is available online.